Networking Concept
What is a Networking ?
Networking is a group of computers or Computers like devices connected together to share the resources like files, printers, services etc.
ARPANET(Advance Research Project Agency Network) is the first compute network of the world.
Advantages of Network
- Reduce the cost of equipment’s –
- File and data security
- Easy Communication and speed
- Share of file, Data, and information.
- Sharing Hardwar
What is Internet ?
It is a world wide , publicly accessible network of interconnected computers networks that transmits data using the standard IP. via Copper wire, fiber Optic Cable, WiFi.
WEB–
Web is one of the service accessible via the Internet.
Intranet –
It is private network that is contained within an enterprise
Extranet
It can be viewed as part of a company’s internet. that is extended to users outside the company like suppliers, venders, customers or other businesses.
Component of Computer Network
Node
An active device attached to a computer network or other telecommunication networks such as a computer or a switch or a point in a network topology at which lions intercept or branch .
Server
A server is computer program which is running to server the requests of other programs the clients, Thus the server performs some computational tasks on behalf of clients. The clients either run on the same computer or connected through the network.

- Server is a main Computer on any network that full fill the request of other computer
Advantages of Server
- BACKUP
- Security
- Storage
Types of Server
Print Server
There are a dozen computers on the network and each one needs to print out a document very few minutes list of the machine that is connected to the network is going to be tied up most of the time. In this case, it makes sense to allocate a machine exclusively to service printers request. The machine is called a printer server.
File Server
- Consider a network of dozen computers. There could be thousands of files scattered across each machine. two Problems arise as follows:
- (a) How do you find the file you need?
- (b) How do you back up your data to keep it safe?
The solution is to keep all your files on one computer. The machine is called the File Server.
Database Server
Many companies rely on a central store of information to run their operations. Information such as sales and stock data is usually kept in a database. Very often a machine will be dedicated to run a specific database. this is called a “Database Server”
Other Kind of Server
A server is any machine that provides a service for other users on the network. Common services include as follows:
- e-mail server
- Internet Proxy Server
- Intranet Server
Network Cable
These are networking hardware used to connect one network devices to other network devices or to concert two or more computers to share Printers, Scanner etc. These devices can be separated by a few meters or nearly unlimited distances.
Network Operating System(NOS)
A network operating system is a computer operating system that is designed primarily to support workstation, personal computer and in a sum instances older terminal that are connected on a LAN(Local Area Network). It can imbedded in a router or hardware firewall that operates the functions in the network layer.
Network Card ( Network Interface Card -NIC)
It is an electronic device that connects a computer to a computer network, usually a LAN. It is considered a piece of computer hardware. Today, most computers have network cards. Network cards enables a computer to exchange data with the network.

Type of Network

LAN(Local Area Network)


A local area network (LAN) is a group of computers and peripheral devices that share a common communications line or wireless link to a server within a distinct geographic area. A local area network may serve as few as two or three users in a home office or thousands of users in a corporation’s central office. Homeowners and information technology (IT) administrators set up LANs so that network nodes can communicate and share resources such as printers or network storage.
LAN networking requires Ethernet cables and Layer 2 switches along with devices that can connect and communicate using Ethernet. Larger LANs often include Layer 3 switches or routers to streamline traffic flows.
A LAN enables users to connect to internal servers, websites and other LANs that belong to the same Wide Area Network (WAN). Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two primary ways to enable LAN connections. Ethernet is an Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) specification that enables computers to communicate with each other. Wi-Fi uses radio waves in the 2.4 gigahertz and 5 GHz spectrum to connect computers to the LAN.
Legacy LAN technologies, including token ring, Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) and Attached Resource Computer Network (ARCNET) have most favor as Ethernet and Wi-Fi speeds increased and connectivity costs decreased
Understanding Local Area Networking
Wired LAN
A wired LAN uses switches and Ethernet cabling to connect endpoints, servers and internet of things (IoT) devices to the corporate network. For small businesses with only a handful of devices, a wired LAN can consist of a single unmanaged LAN switch with enough Ethernet ports to interconnect all devices. But larger LANs that connect thousands of devices require additional hardware, software and configuration steps to ensure the network is performing optimally. This is where the concept of virtual LANs (VLANs) comes into play.
Because an Ethernet LAN is a shared medium, if an organization has too many devices connected to a single LAN, the amount of broadcast traffic — which is heard by all devices on the LAN — can create congestion and bottlenecks. To alleviate the amount of broadcast traffic being sent and received on a LAN, the network can be broken into multiple VLANs. This condenses the broadcast traffic so it’s only heard by other devices within that virtual LAN — not the entire network. This eliminates much of the broadcast overhead that can lead to performance problems.
Wireless LAN
Wireless LANs use the IEEE 802.11 specification to transport data between end devices and the network using wireless spectrum. In many situations, a wireless LAN is preferable to a wired LAN connection because of its flexibility and cost savings, as it isn’t necessary to run cabling throughout a building. Companies assessing WLANs as a primary means of connectivity often have users who rely exclusively on smartphones, tablets and other mobile devices.
The benefits of using LAN
Local area networks enable devices to connect, transmit and receive information between them. The benefits of LAN technologies include the following:
- Enable access to centralized applications residing on servers;
- Enable all devices to store business-critical data in a centralized location;
- Allow resource sharing, including printers, apps and other shared services;
- Allow multiple devices on a LAN to share a single internet connection; and
- Protect LAN-connected devices using network security tools
WAN (Wide Area Network)
A wide area network connects business locations that are dispersed throughout a state, country or even globally. The organization purchases WAN services from a telecommunications provider that manages the operational status of each WAN link. In most cases, only network traffic that must be transported back and forth between business locations is moved over the WAN. Due to potential latency issues, geographically dispersed locations typically are built with their own internet connection. That way, internet-bound data can be directly sent to and from a branch office, instead of having it backhauled to a central office.
The technologies used to build WANs can include MPLS(Multiprotocol Label Switching), Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS), Ethernet over Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) and satellite-based technologies. Since the carrier typically handles the underlying technologies, to the end customer, the WAN looks like a standard Ethernet connection between locations.


MAN(Metropolitan Area Network)

MAN stands for A metropolitan area network. In this network all users communicate in an area larger than LAN(Local Area Network). It may be cover the area of several buildings in the same city.
It is larger than LAN but smaller than WAN(Wide Area Network)
MAN generally used connects a number of local area networks (LANs) together by using high-speed technology, such as a fiber-optical link. A MAN may be operated by one organization, but generally, it will be used by many companies and organizations. MAN usually used to communicate many LANs together. It can be used in television cables
MAN stands for A metropolitan area network. In this network all users communicate in an area larger than LAN(Local Area Network). It may be cover the area of several buildings in the same city.
Types of MAN
There are some types of MAN.
• Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
• Fiber Distribution Data Interface (FDDI)
• Switched multi-megabit data service (SMDS)
Where is the man network used?
A LAN(Local Area Network) mostly used in banks, hospitals, office buildings, schools, and rooms. A MAN(A metropolitan area network ) is usually used in cities. The WAN in different countries, cities, and states. MAN mostly used for business purposes. It is used to connect one business branch to another branch.
Advantages of MAN(Metropolitan Area Network)
- It is less expensive than WAN
- It is used to send a local e-mail.
- It has high speed than WAN
- It provides high security.
- It covers a large area than LAN
- It provides centralized data storage.
- It enables you to connect many fast LANs together.
- It utilizes the disable advantages of both LAN and WAN to provide an efficient network.
- There is less implementation cost than LAN and WAN because it required fewer resources than WAN and LAN.
- It provides common sharing of resources like printer etc.
Disadvantages of Man(Metropolitan Area Network)
- It is difficult to manage when we have large network.
- For its installation we need skilled or experts and also required a network administrator. They all increase the overall installation and management costs.
- Ir requires larger cable than LAN.
- It is difficult to make a system secure or safe from hackers and unauthorized users.
- The main disadvantage of MANs is the cost of cutting-edge technology employed.
- Technical staff required.
SAN

A Storage Area Network or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage
CAN

A campus network is a computer network made up of an interconnection of LAN’s within a limited geographical area. The networking equipment (switch, Router) and transmission media (optical fiber, UTP) are almost entirely owned by the campus: Academic Building , Library, Hostel, Examination Section, Admission Section et
Deference Between LAN MAN WAN

Network Topology

What is Network Topology?
The term “Topology” refers to the way a network is laid out, either physically or Logically.
Topology can be referred as the geometric arrangement of a computer system. each computer system in a topology is known as node
Types of Network Topology
There are several different logical and physical network topologies from which administrators can choose to build a secure, robust, and easily maintainable topology. The most popular configurations include:
Bus network topology
Also known as backbone network topology, this configuration connects all devices to a main cable via drop lines. The advantages of bus network topology lie in its simplicity, as there is less cable required than in alternative topologies, which makes for easy installation.
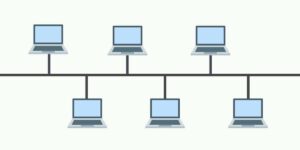
Advantage
Easy installation
Fewer cables required than Mesh and star topology
Good for small businesses
Low cost
Easy to manage and expand
Disadvantage
Backbone performance is critical
Easily congested on busy periods
Efficiency decreases rapidly with each added node
Efficiency decreases rapidly with each added node
Ring network topology
The most common network topology, star topology connects each device in the network to a central hub. Devices can only communicate with each other indirectly through the central hub.

Advantage
- Low incidence of collision
- Suitable for small businesses
- Low cost
- Dual ring option provides continuity through redundancy
Disadvantage
- One faulty node will bring the entire network down
- Requires extensive preventative maintenance and monitoring
- Performance declines rapidly with each additional node
- Reorganizing the network requires a full system shutdown
Star network topology
A star topology is a topology where every node in the network is connected to one central switch. Every device in the network is directly connected to the switch and indirectly connected to every other node. The relationship between these elements is that the central network hub is a server and other devices are treated as clients. The central node has the responsibility of managing data transmissions across the whole network and acts as a repeater. With star topologies, computers are connected with a coaxial cable, twisted pair, or optical fiber cable.

Advantage
- Easy to manage from one point – the switch
- Easy to add and remove nodes
- Low cost
- Durable
- Low cable usage
- Good for small businesses
Disadvantage
- Requires specialist network hardware (the switch)
- Makes the network reliant on the switch’s performance
- Performance declines rapidly with each additional node
- A finite number of switch ports limits the network’s size.
Mess Topology
It is also known as completely interconnected topology. In Mess topology. every node has a dedicated point to point link to every other node. it provides a bi-directional link between each possible node. This type of network topology contains at least two nodes with two or more paths between them. Mess topology is robust because the failure of any one computer does not bring down the entire network.

Advantage
Excellent for long distance networking
Communication possible through the alternate route, if one path is busy
Disadvantage
Long wire/cable length, hence increase in the cost of installation and maintenance.
There are high chance of redundancy in many of network connections.
Tree Topology
This is a network topology in which nodes are arranged as a tree. the function of the central node in this topology may be distributed. A tree topology is an extension and variation of star topology. Its basic structure is like and inverted tree, where the root acts as a server. it allows more devices to be attached to a single hub.

Advantage
- The tree topology simulates hierarchical flow of data. So it is suitable for application where hierarchical flow of data and control are required.
- We can easily extend the network.
Disadvantag
- Long cables are required.
- there are dependencies on the root node.
- If the central hub fails , the entire system breaks down.
Data Communication
It is the exchange of data between two devices using some form of transmission media. It includes the transfer of data or information and the method of preservation of data during the transfer process. The transmission of data is done between a centralized computer and remote terminals or between two or more computers centers over established communication links.
Data is transferred from one place to another in the form of signals There are Three types of signals as follows:
Digital Signal
In digital signal, data is transmitted in the electronic form of data i.e. binary digits(0 or 1)

Analog Signal
In analog signal, data is transmitted in the form of radio waves like in telephone line

Hybrid Signal
Hybrid signal has properties of both analog signal and digital signal.

Communication Channel
Communication Channel refers to the direction of signal flow between two linked devices. there are mainly three types of communication channel as follows:
Simplex Channel
In this channel, the flows of data is always in one direction, with no capability to support response in other direction.
This Communication is unidirectional.
Only one of the communicating device transmits information and the other can only receive it. e.g. Keyboard, Radio, TV.

Half Duplex Channel
in this channel the data can flow in Both directions, but not at a same time.
When one device transmits information , then other can only receive at that point of time. e.g. Walkie-Talkie.

Full Duplex Channel
In this channel the flow of data is in both direction at a same time i.e. both satiations can transmit and receive information simultaneously. e.g. Mobile Phone

Communication Media
Communication media of a network refers to the transmission media or the connecting media used in the network. It can be broadly defined as anything that can carry information from source to destination. It refers to the physical media through which communication signal can be transmitted from one point to another.
Communication media can be divided into two broad category which are as follows.
Guided media or wired Technology
- Ethernet or Twisted Pair Cable
- Co- Axial Cable
- Fiber Optic Cable
Unguided Media or Wireless Media
- Radio transmission
- Microwave Transmission
- Satellite Communication
- Infrared Wave Transmission
- Bluetooth
Guided media or wired Technology
he data signal is guided media is bound by the cabling system that guides the data signal along a specific path. It consists of a cable composed of metals like Copper tin or silver.
Basically, De can be divided into three categories which are as follows
(1) Ethernet cable or twisted pair cable
MDS cable wire or twisted together which are surrounded by an insulating material and an outer layer called jacket stop, a twisted pair consists of two conductors of copper.
One of the devices is used to carry a signal to the receiver and the other is used only as a ground reference. It is used as a short distance communication that is local area network used to twisted pair cable


Advantage
- Simple in its structure.
- Physically flexible.
- Can we easily corrected.
- Has low weight.
- Low cost.
Disadvantage
- Due to high attenuation, signal cannot be transported over a long distance without using repeater.
- Due to Low bandwidth, it is unsuitable for broadband application
- Data rates supported are 1 Mbps to 10 Mbps.
(2) Co-axial Cable
Carry the signal frequency data communication through the network. Which consists of a solid wire code surrounded by foil shield for conducting braid or wire mesh, each separated by some insulator.
It has a signal inner conductor that transmits electrical signals and the outer conductor act as a ground which is wrapped in a sheath of Teflon or PVC. Coaxial Cable is commonly used in transporting multi-Channel television Signal in cuties.

Advantage
- Transmission quality of co-axil cable is better than twisted pair cable.
- Can be successfully used for shared cable network.
- Can transmit several channels simultaneously, so can be used for broadband transmission.
Disadvantage
- It is expensive compared to twisted pair cable
- These are not compatible with twisted pair cable..
Fiber Optical Cable

It is made up of glass or plastic and transmits signals in the form of light from a source at one end to another end.
At the source, there are either Light Emitting Diodes(LED) or Laser Diode(LD), which modulate the data into light beam using frequency modulation techniques.
An optical fibre consists of a very narrow stand of glass called the core.
The surrounding core is a concentric layer of glass called the Cladding. Cladding is covered by a protective coating of plastic, known as Jacket.
Optical Fiber allows transmission over longer distance at higher bandwidth which is not agented by electromagnetic field. the speed of optical fiber is hundred of times faster than co-axil cables.
Advantage
- It is immune to electrical and magnetic fields. So the data does not get disturbed and pure data is retrieved on the other end.
- Highly suitable for harsh industrial environment.
- It guarantees secure transmission and has a very high transmission capacity.
- It can be used for broadband transmission, where several channels are handled in parallel.
Disadvantage
- Connecting two fibre or a light source to a fibre is difficult.
- Because of noise immunity these are virtually impossible to tap.
- thes are ecpensive to install but last longer thane capper calble.
- Optical fiblre require more protection around the cable compared to copper cable.
Unguided Media or Wireless Technologies
It is the transfer of information over a distance without the use of enhanced electrical conductors or wires. When the computers in a network are interconnected and data is transmitted through waves, then they are said to be connected through unguided media. Basically, they can be further divided into various categories which are as follows:
(i) Radio Wave Transmission
When two terminals communicate by using radio frequencies then such type of communication is known as radiowave transmission. This transmission is also known as Radio Frequency (RF) transmission.
These are omnidirectional, Radio Waves, particularly those waves that propagate in the sky mode, can travel long distances. Each computer attaches to an antenna that can both send and receive radio transmission.
Radiowave transmission set-up has two parts as follows:
Transmitter Devices which transmit signals are termed as transmitter.
Receiver Devices which received signals are termed as receiver
Advantage
- Cheaper than wired network
- Provides mobility
- Easy to use over difficult terrain
Disadvantage
- Insecure communication can be easily taped.
- It is affected by the weather conditions such
as rain, storms, thunder etc.
Microwave Transmission

Microwaves are electromagnetic waves having frequencies range from 0.3 to 300 GHz. Microwaves are unidirectional.
These have a higher frequency than that of radio waves. Microwave is one of the fastest media for data transmission over communication channel. They can be aimed at a single direction instead of broadcasting in all directions. Microwave antenna is placed on the top of buildings. It consists series of stations approx. 30 miles apart. It is used in cellular network and television broadcasting
Advantage
- Cheaper than digging trenches for laying cables and using repeaters.
- Using microwave, communication is possible even in difficult terrains.
Disadvantage
- Insecure communications, microwaves is easy.
- It is affected by the weather conditions such as rain, thunder, storm etc.
- Cost of maintenance, implementation and design is high..
Satellite Communication
The communication across longer distances can be provided by combining radio frequency transmission with satellites. It works over a long distance and fast communication. It amplifies signal received from one earth station and again, retransmits to another earth station, which can be located many thousands of miles away. It is used for communications to ships, vehicles,
planes and handheld terminals.

Advantage
- It covers a vast range of area.
- The wired communication is almost impossible and too costly to use across the continents where the satellite communication proves to be the best alternatives.
- It is very useful in television transmission.
Disadvantage
- It is very costly. So, it is preferred to use personal or low budget communication.
- There is atmospheric loss of transmitted signals.
Infrared Wave Transmission

Infrared waves are the high frequency waves used for short-range communication. These waves do not pass through the solid-objects. They are mainly used in TV remote and wireless speakers.
Advantage
- Power consumption is less.
- Circuitry cost is less
- Circuitry is simple
Disadvantage
- Line of sight, need to be in a straight line for communication.
- Limited in a short range.
- Can be blocked by common materials like walls, people, plants etc.
Bluetooth

It is a wireless technology used for exchanging data over short distances to create a Personal Area Network. It can connect several devices, overcoming problems of synchronization.
Advantage
- We are able to share data without any cord.
- We are able to share data without disclosing our private data.
- We can use Bluetooth on many different devices as it is mostly in all devices such as laptops, cell phones, music player, hand sets, printers and a lot more other products.
Disadvantage
- Battery consumption, as it is the most common mode of data transfer in these days, so it is left enabled in the devices, which consumes more battery. It can be remedied by disabling Bluetooth after use.
- Bluetooth Internet is very slow, so it is suggested not to go for Bluetooth Internet.
Network Connection
There are mainly three ways of network connection:-
Dial- Up Connection
Broad Band Connection
Wireless Connection
Dial- Up Connection

A dial-up connection is a temporary connection, set-up between your computer and ISP server.
Dial-up connection uses the telephone line (Public Switched Telephone Network-PSTN) to connect to the Internet. The modem connects the computer through the standard phone lines, which serves as the data transfer medium.
When a user initiates a dial-up connection, user needs to enter the password and specify a username and modem dials a phone number of an Internet Service Provider (ISP) that is designated to receive dial-up calls. The ISP then establishes the connection, which usually takes about 10 seconds and is accompanied by several beeping and buzzing sounds
Broadband Connection
The term broadband commonly refers to high speed Internet access that is always on and faster than the traditional dial-up access. It is the short form of broad bandwidth that uses a telephone line to connect to the Internet. Speed of broadband connection is measured in Mbps (Megabits per second).Broadband access allows users to connect to the Internet at greater speed than a standard 256 Kbps (Kilobits per second) modem or dial-up access. Broadband access requires the use of a broadband modem.
Broadband includes several high speed transmission technologies such as follows:
Digital Subscriber Line
- DSL is a popular broadband connection. It provides Internet access by transmitting digital data over the wires of a local telephone network. DSL uses the existing copper telephone lines for Internet access.
- BSNL, Airtel, Reliance, MTNL are DSL broadband service providers in India.
- Faster forms of DSL typically available to businesses are as follows:
- High Data Rate Digital Subscriber Line (HDSL)
- Very High Data Rate Digital Subscriber Line(VHDSL)
- Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL)
- Symmetrical Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL)
Cable Modem
This service enables cable operators to provide broadband using the same co-axial cables, that deliver pictures and sound to your TV set. A cable modem can be added to or integrated with a set-top box that provides your TV set for Internet access. They provide transmission speed of 1.5 Mbps or more.
Broadband Over Power Line(BPL)
BPL is the delivery of broadband over the existing low and medium voltage electric power distribution network. BPL speeds are comparable to DSL and cable modem speeds.
BPL can be provided to homes using existing electrical connections and outlets. It is also known as power-band. BPL is good for those areas, where there are no broadband connections, but infrastructure exists. e.g. in rural areas. power
Wireless Connection
Wireless broadband connects a home or business to the Internet using a radio link between the customer’s location and the service provider’s facility. Wireless broadband can be mobile or fixed. Unlike DSL and cable, wireless broadband requires neither a modem nor cables. Some way to connect the internet wirelessly are as follows:
